

Pamela A. Davol, 76 Mildred Avenue, Swansea,
MA 02777-1620.
pdavol@labbies.com
The American Kennel Club classifies a Labrador Retriever into three color categories; what is known in genetic analysis as phenotypes. Phenotype can therefore be defined as the actual color appearance. However, when one breeds two black Labs, one may get only black puppies, but upon breeding another two black individuals one may get yellow and chocolate puppies as well as black. This indicates that though the dogs from two such crosses may appear to be the same color, or phenotype, they don't have the same genetic makeup, or genotype. It is the genotypes of the sire and dam which are responsible for yielding color variations in a litter.
It is not by accident that there are more black Labradors than any other color or that many breeders prefer black over the other colors. Since the black coloration is prevalent, "type" has been well substantiated in black Labs for many years, with yellows following and recently in chocolates. But the question remains: why is black prevalent? There are two genes responsible for black or chocolate coloration in the Lab. "B" which is the symbol for the black gene and "b" which symbolizes the chocolate gene. Knowing that a puppy gets 1/2 of its genes from one parent and 1/2 from the other parent then if one crosses a black Lab that has no chocolate gene to a chocolate Lab an individual might expect to get black and chocolate puppies; instead, the individual may be disappointed to find that the litter is all black. Where did the chocolate disappear to? If this individual is not discouraged he may later breed one of these black puppies to a chocolate lab and this time he will be satisfied because 1/2 of the litter will be black and 1/2 will be chocolate. The chocolate had been hiding. This indicates that although we cannot see the chocolate, it is still there in the genetic make-up (genotype), masked by the black gene. For this reason, geneticists call the black gene dominant over the chocolate gene which is called recessive. To summarize:
BB = black Lab, no chocolate gene Bb = black Lab, carries chocolate gene bb = chocolate Lab, no black gene
To discuss yellow coloration, a third gene must be introduced. Yellow is produced by the presence of a recessive epistatic gene which has the effect of blotting out the expression of the black or chocolate genes. If "E" = the dominant form of for the epistatic gene, and "e" = the recessive form, then there are three possibilities:
EE = no yellow gene Ee = yellow carrier but apears either black or chocolate ee = yellow Lab
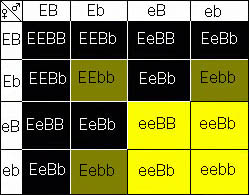
There are only three acceptable colors (phenotypes) for Labrador Retrievers, however, there are a total of nine possible combinations of genes (genotypes) that will determine which of these colors a Lab will be (Figure 1). Of those nine, there is one combination that should be avoided when breeding, that is the yellow dog carrying two recessive chocolate genes (eebb). This combination will produce a yellow Lab with chocolate pigmentation of the nose and eye-rims, so one should avoid any breeding cross that will produce individuals with this genetic make-up. But how can a breeder be certain? He can't, that's why breeding is very tricky. It is often difficult to determine genetic make-up of an individual; even when a line is researched there may still be some question. A breeder may produce individuals with undesirable coat traits, but with his knowledge of genetics he will know why the trait appeared and will not repeat the mistake. The Appendix gives examples of the possible crosses of genotypes and what one may expect when breeding particular individuals in terms of the ratio of genotypes within the litter as well as the ratio of color expression (phenotype) within the litter. If one knows the genotype of one's Lab, than he may determine the expected outcome of color variation when he crosses that Lab to another of a particular genotype.
 =
= or
or or
or or
or
 =
= or
or or
or
 =
= or
or
The following are the 81 possible crosses between dog and bitch for coat color and the anticipated litter outcome:
Key:
{sire's genotype(color)} X {dam's genotype(color)} = frequency of genotypes within the litter---% breakdown of color expression within the litter (phenotype)
1. EEBB(black) X EEBB(black) = genotype: all EEBB---phenotype: all black puppies
2. EEBB(black) X EeBB(black/yellow carrier) = genotype: 1/2 EEBB + 1/2 EeBB---phenotype: all black puppies
3. EEBB(black) X EEBb(black/choc carrier) = genotype: 1/2 EEBB + 1/2 EEBb---phenotype: all black puppies
4. EEBB(black) X EeBb(black/yellow & choc carrier) = genotype: 1/4 EEBB + 1/4 EeBB + 1/4 EEBb + 1/4 EeBb---phenotype: all black puppies
5. EEBB(black) X eeBB(yellow/black carrier) = genotype: all EeBB---phenotype: all black puppies
6. EEBB(black) X eeBb(yellow/black & choc carrier) = genotype: 1/2 EeBB + 1/2 EeBb---phenotype: all black puppies
7. EEBB(black) X eebb(yellow/choc carrier) = genotype: all EeBb---phenotype: all black puppies
8. EEBB(black) X EEbb(choc) = genotype: all EEBb---phenotype: all black puppies
9. EEBB(black) X Eebb(choc/yellow carrier) = genotype: 1/2 EEBb + 1/2 EeBb---phenotype: all black puppies
10. EeBB(black/yellow carrier) X EEBB(black) = see # 2.
11. EeBB(black/yellow carrier) X EeBB(black/yellow carrier) = genotype: 1/4 EEBB + 1/2 EeBB + 1/4 eeBB---phenotype: 75% black pups + 25% yellow pups
12. EeBB(black/yellow carrier) X EEBb(black/choc carrier) = genotype: 1/4 EEBB + 1/4 EEBb + 1/4 EeBB + 1/4 EeBb---phenotype: all black puppies
13. EeBB(black/yellow carrier) X EeBb(black/yellow & choc carrier) = genotype: 1/8 EEBB + 1/8 EEBb +1/4 EeBB + 1/4 EeBb + 1/8 eeBB + 1/8 eeBb---phenotype: 75% black pups + 25% yellow pups
14. EeBB(black/yellow carrier) X eeBB(yellow/black carrier) = genotype: 1/2 EeBB + 1/2 eeBB---phenotype: 50% black pups + 50% yellow pups
15. EeBB(black/yellow carrier) X eeBb(yellow/black & choc carrier) = genotype: 1/4 EeBB + 1/4 EeBb +1/4 eeBB + 1/4 eeBb---phenotype: 50% black pups + 50 % yellow pups
16. EeBB(black/yellow carrier) X eebb(yellow/choc carrier) = genotype: 1/2 EeBb + 1/2 eeBb---phenotype: 50% black pups + 50% yellow pups
17. EeBB(black/yellow carrier) X EEbb(choc) = genotype: 1/2 EEBb + 1/2 EeBb---phenotype: all black puppies
18. EeBB(black/yellow carrier) X Eebb(choc/yellow carrier) = genotype: 1/4 EEBb + 1/2 EeBb + 1/4 eeBb---phenotype: 75% black pups + 25% yellow pups
19. EEBb(black/choc carrier) X EEBB(black) = see # 3.
20. EEBb(black/choc carrier) X EeBB(black/yellow carrier) = see # 12.
21. EEBb(black/choc carrier) X EEBb(black/choc carrier) = genotype: 1/4 EEBB + 1/2 EEBb + 1/4 EEbb---phenotype: 75% black pups + 25% choc pups
22. EEBb(black/choc carrier) X EeBb(black/yellow & choc carrier) = genotype: 1/8 EEBB + 1/4 EEBb + 1/8 EeBB + 1/4 EeBb + 1/8 EEbb + 1/8 Eebb---phenotype: 75% black pups + 25% choc pups
23. EEBb(black/choc carrier) X eeBB(yellow/black carrier) = genotype: 1/2 EeBB + 1/2 EeBb---phenotype: all black puppies
24. EEBb(black/choc carrier) X eeBb(yellow/black & choc carrier) = genotype: 1/4 EeBB + 1/2 EeBb + 1/4 Eebb---phenotype: 75% black pups + 25% choc pups
25. EEBb(black/choc carrier) X eebb(yellow/choc carrier) = genotype: 1/2 EeBb + 1/2 Eebb---phenotype: 50% black pups + 50% choc pups
26. EEBb(black/choc carrier) X EEbb(choc) = genotype: 1/2 EEBb + 1/2 EEbb---phenotype: 50% black pups + 50% choc pups
27. EEBb(black/choc carrier) X Eebb(choc/yellow carrier) = genotype: 1/4 EEBb + 1/4 EeBb + 1/4 EEbb + 1/4 Eebb---phenotype: 50% black pups + 50% choc pups
28. EeBb(black/yellow & choc carrier) X EEBB(black) = see # 4.
29. EeBb(black/yellow & choc carrier) X EeBB(black/yellow carrier) = see # 13.
30. EeBb(black/yellow & choc carrier) X EEBb(black/choc carrier) = see # 22.
31. EeBb(black/yellow & choc carrier) X EeBb(black/yellow & choc carrier) = genotype: 1/16 EEBB + 1/8 EEBb + 1/8 EeBB + 1/4 EeBb + 1/16 eeBB + 1/8 eeBb + 1/16 eebb + 1/16 EEbb + 1/8 Eebb---phenotype: 55% black pups + 25% yellow pups + 20% choc pups
32. EeBb(black/yellow & choc carrier) X eeBB(yellow/black carrier) = genotype: 1/4 EeBB + 1/4 EeBb + 1/4 eeBB + 1/4 eeBb---phenotype: 50% black pups + 50% yellow pups
33. EeBb(black/yellow & choc carrier) X eeBb(yellow/black & choc carrier) = genotype: 1/8 EeBB + 1/4 EeBb + 1/8 eeBB + 1/4 eeBb + 1/8 eebb + 1/8 Eebb---phenotype: 50% yellow pups + 38% black pups + 12% choc pups
34. EeBb(black/yellow & choc carrier) X eebb(yellow/choc carrier) = genotype: 1/4 EeBb + 1/4 Eebb + 1/4 eeBb + 1/4 eebb---phenotype: 25% black pups + 50% yellow pups + 25% choc pups
35. EeBb(black/yellow & choc carrier) X EEbb(choc) = genotype: 1/4 EEBb + 1/4 EeBb + 1/4 EEbb + 1/4 Eebb---phenotype: 50% black pups + 50% choc pups
36. EeBb(black/yellow & choc carrier) X Eebb(choc/yellow carrier) = genotype: 1/8 EEBb + 1/4 EeBb + 1/8 eeBb + 1/8 eebb + 1/8 EEbb + 1/4 Eebb---phenotype: 37.5% black pups + 25% yellow pups + 37.5% choc pups
37. eeBB(yellow/black carrier) X EEBB(black) = see # 5.
38. eeBB(yellow/black carrier) X EeBB(black/yellow carrier) = see # 14.
39. eeBB(yellow/black carrier) X EEBb(black/choc carrier) = see # 23.
40. eeBB(yellow/black carrier) X EeBb(black/yellow & choc carrier) = see # 32
41. eeBB(yellow/black carrier) X eeBB(yellow/black carrier) = genotype: all eeBB---phenotype: all yellow puppies
42. eeBB(yellow/black carrier) X eeBb(yellow/black & choc carrier) = genotype: 1/2 eeBB + 1/2 eeBb---phenotype: all yellow puppies
43. eeBB(yellow/black carrier) X eebb(yellow/choc carrier) = genotype: all eeBb---phenotype: all yellow puppies
44. eeBB(yellow/black carrier) X EEbb(choc) = genotype: all EeBb---phenotype: all black puppies
45. eeBB(yellow/black carrier) X Eebb(choc/yellow carrier) = genotype: 1/2 EeBb + 1/2 eeBb---phenotype: 50% black pups + 50% yellow pups
46. eeBb(yellow/black & choc carrier) X EEBB(black) = see # 6.
47. eeBb(yellow/black & choc carrier) X EeBB(black/yellow carrier) = see # 15.
48. eeBb(yellow/black & choc carrier) X EEBb(black/choc carrier) = see # 24.
49. eeBb(yellow/black & choc carrier) X EeBb(black/yellow & choc carrier) = see # 33
50. eeBb(yellow/black & choc carrier) X eeBB(yellow/black carrier) = see # 42.
51. eeBb(yellow/black & choc carrier) X eeBb(yellow/black & choc carrier) = genotype: 1/4 eeBB + 1/2 eeBb + 1/4 eebb---phenotype: all yellow puppies
52. eeBb(yellow/black & choc carrier) X eebb(yellow/choc carrier) = genotype: 1/2 eeBb + 1/2 eebb---phenotype: all yellow puppies
53. eeBb(yellow/black & choc carrier) X EEbb(choc) = genotype: 1/2 EeBb + 1/2 Eebb---phenotype: 50% black pups + 50% choc pups
54. eeBb(yellow/black & choc carrier) X Eebb(choc/yellow carrier) = genotype: 1/4 EeBb + 1/4 Eebb + 1/4 eeBb + 1/4 eebb---phenotype: 25% black pups + 25% choc pups + 50% yellow pups
55. eebb(yellow/choc carrier) X EEBB(black) = see # 7.
56. eebb(yellow/choc carrier) X EeBB(black/yellow carrier) = see # 16.
57. eebb(yellow/choc carrier) X EEBb(black/choc carrier) = see # 25.
58. eebb(yellow/choc carrier) X EeBb(black/yellow & choc carrier) = see # 34
59. eebb(yellow/choc carrier) X eeBB(yellow/black carrier) = see # 43.
60. eebb(yellow/choc carrier) X eeBb(yellow/black & choc carrier) = see # 52.
61. eebb(yellow/choc carrier) X eebb(yellow/choc carrier) = genotype: all eebb---phenotype: all yellow puppies
62. eebb(yellow/choc carrier) X EEbb(choc) = genotype: all Eebb---phenotype: all choc puppies
63. eebb(yellow/choc carrier) X Eebb(choc/yellow carrier) = genotype: 1/2 Eebb + 1/2 eebb---phenotype: 50% choc pups + 50% yellow pups
64. EEbb(choc) X EEBB(black) = see # 8.
65. EEbb(choc) X EeBB(black/yellow carrier) = see # 17.
66. EEbb(choc) X EEBb(black/choc carrier) = see # 26.
67. EEbb(choc) X EeBb(black/yellow & choc carrier) = see # 35
68. EEbb(choc) X eeBB(yellow/black carrier) = see # 44.
69. EEbb(choc) X eeBb(yellow/black & choc carrier) = see # 53.
70. EEbb(choc) X eebb(yellow/choc carrier) = see # 62.
71. EEbb(choc) X EEbb(choc) = genotype: all EEbb---phenotype: all choc puppies
72. EEbb(choc) X Eebb(choc/yellow carrier) = genotype: 1/2 EEbb + 1/2 Eebb---phenotype: all choc puppies
73. Eebb(choc/yellow carrier) X EEBB(black) = see # 9.
74. Eebb(choc/yellow carrier) X EeBB(black/yellow carrier) = see # 18.
75. Eebb(choc/yellow carrier) X EEBb(black/choc carrier) = see # 27.
76. Eebb(choc/yellow carrier) X EeBb(black/yellow & choc carrier) = see # 36
77. Eebb(choc/yellow carrier) X eeBB(yellow/black carrier) = see # 45.
78. Eebb(choc/yellow carrier) X eeBb(yellow/black & choc carrier) = see # 54.
79. Eebb(choc/yellow carrier) X eebb(yellow/choc carrier) = see # 63.
80. Eebb(choc/yellow carrier) X EEbb(choc) = see # 72.
81. Eebb(choc/yellow carrier) X Eebb(choc/yellow carrier) = genotype: 1/4 EEbb + 1/2 Eebb + 1/4 eebb---phenotype: 75% choc pups + 25% yellow pups